F1 Generation And F2 Generation
The chief deviation between F1 and F2 generation is that F1 generation is the first filial generation of the offspring from the parents. But, F2 generation is the second filial generation of the offspring, generated through inbreeding of F1 individuals. Furthermore, the F1 generation is distinctly unlike from the parental types. In contrat, the F2 generation may showroom some parental phenotypes. Moreover, the F1 generation is important in hybridization, obtaining the best characteristics of parents in the offspring. Meanwhile, F2 generation is important in inbreeding in order to maintain stable traits over generations.
In brief, F1 and F2 generation are ii generations of the offspring of a dihybrid cantankerous. Here, a dihybrid cross or a two traits cross is a genetic cross washed between 2 individuals that are identically hybrid for 2 traits.
Key Areas Covered
one. What is the F1 Generation
– Definition, Genetics, Importance
2. What is F2 Generation
– Definition, Genetics, Importance
iii. What are the Similarities Between F1 and F2 generation
– Outline of Common Features
4. What is the Difference Between F1 and F2 Generation
– Comparison of Key Differences
Primal Terms
Dihybrid, F1 Generation, F2 Generation, Hybridization, Inbreeding, Outbreeding 
What is the F1 Generation
The F1 generation is the first filial generation of the dihybrid cross. Hither, a dihybrid cross is a genetic cantankerous, which focuses on the inheritance of two independent traits. Therefore, information technology describes the second constabulary of Mendel; The Independent Assortment.
Genetics
Generally, the parents used in a dihybrid cross are identically hybrid for the 2 traits testing. Hence, they produce two types of gametes that are the ascendant grade and recessive class for both traits. Likewise, the F1 generation shows a single genotype, which is heterozygous for both traits. Later on, its phenotype shows dominant phenotypes of both traits.
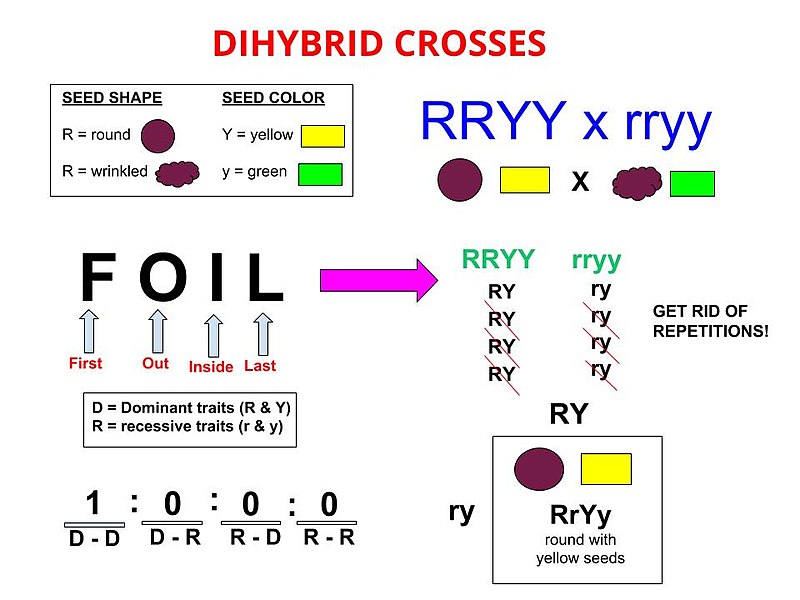
Figure i: F1 Generation
Hybridization
Importantly, F1 generation shows increased heterozygosity, which in plough increases the vigor . Therefore, hybridization is the genetic process, which results in the F1 generation. Furthermore, h ybridization is ane of the two methods of selective convenance. More specifically, in hybridization, breeding occurs between two parents that are genetically different. Moreover, the parents may belong to different breeds or cultivars within the aforementioned species. Also, the resulting offspring is known as the hybrid .
Outbreeding
Besides, the convenance method, which involves unrelated organisms is outbreeding. Every bit outbreeding combines the characteristics of different pure breeds, it increases the variation of a grouping of organisms through mating. Basically, the breeding of individuals in ii populations of the same genus is an example of outbreeding. Yet, outbreeding makes more heterozygous allele combinations inside the offspring, randomly mixing all the possible alleles found in the population. Withal, outbreeding depression is the main disadvantage of outbreeding in which the production of unsuitable traits for the nowadays habitat is produced that reduces the fitness to the environment.
What is F2 Generation
The F2 generation is the 2nd filial generation of the dihybrid cantankerous. Significantly, it is the offspring produced past crossing individuals of the F1 generation.
Genetics
In comparing, the F2 generation is the second filial generation of the dihybrid cantankerous, producing through inbreeding of individuals of the F1 generation. Hence, the 4 types of gametes produced by the F1 generation comprise all combinations of dominant and recessive forms of the ii testing traits. On the other hand, F2 generation shows a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1, having 9 individuals with both dominant traits, iii individuals in two sets with one dominant and 1 recessive trait and one private with both traits recessive respectively.
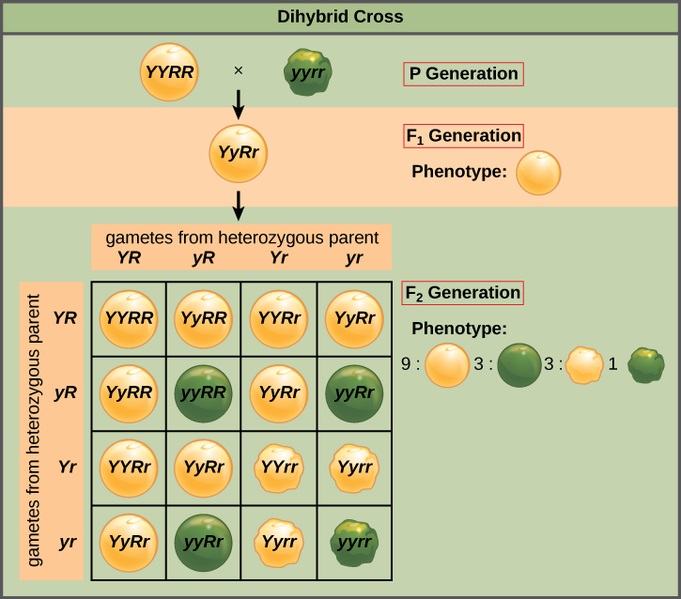
Figure ii: Dihybrid Cantankerous
Inbreeding
Furthermore, i nbreeding is the other method of selective breeding opposite to hybridization or outbreeding. Basically, it involves breeding from closely-related animals, especially over many generations. Importantly, it increases the homozygosity of the offspring. Hence, inbreeding can be used to maintain pure lines. Therefore, the main purpose of inbreeding is to maintain the desired characteristics of parents in the offspring. For example, domestic dog breeders, horse breeders, and the breeders of exotic animals oftentimes use inbreeding to increase a desired genetic trait from the parents in the offspring. However, the negative side furnishings of inbreeding include the emphasizing of the undesirable characteristics of the parents, such as concrete and mental abnormalities in the offspring.
Similarities Between F1 and F2 generation
- F1 and F2 generation are the ii generations of the offspring of a dihybrid cross.
- The parents of the dihybrid cross are identically hybrid for two traits.
- Also, a dihybrid cross is performed to draw the inheritance of 2 traits.
- In the Mendelian inheritance, a dihybrid cross describes the 2d Law or the Police force of Independent Assortment.
Departure Between F1 and F2 Generation
Definition
F1 generation refers to the showtime filial generation of the offspring from the parents, while F2 generation is the second filial generation of the offspring, generated through inbreeding of F1 individuals.
Method of Crossing
The F1 generation is a result of outbreeding, but F2 generation is a issue of inbreeding.
Parents
The parents of the F1 generation are two individuals that are identically hybrid for two traits, while the parents of the F2 generation are the individuals of the F1 generation.
Genetic Similarity of Parents
The F1 generation is a result of a cross between genetically dissimilar parents, simply F2 generation is a issue of a cross betwixt genetically similar parents.
Genetics of the Parents
1 parent of the F1 generation is homozygous dominant for both traits while the 2nd is homozygous recessive. In contrast, the parents of the F2 generation are heterozygous for both traits.
Gametes
The 2 types of gametes that form the F1 generation are YR and yr, while the iv types of gametes that form the F2 generation are YR, Yr , yR , and year.
Genotypic Ratio
F1 generation shows a single genotype; RrYy , which is heterozygous for both traits. Meanwhile, F2 generation shows RRYY i: RRYy 2: RRyy 1: RrYY 2: RrYy 4: Rryy 2: rrYY 1: rrYy two: rryy 1
Phenotypic Ratio
F1 generation shows a single phenotype with dominant characteristics for both traits, while F2 generation shows a phenotypic ratio 9:3:3:1.
The Similarity of Phenotypes to the Parents
The F1 generation is distinctly different from the parental types, but the F2 generation may exhibit some parental phenotypes.
Result to the Vigor
F1 generation has an increased vigor, while the F2 generation has a decreased vigor .
Importance
The F1 generation is of import in hybridization, obtaining the best characteristics of parents in the offspring. Meanwhile, the F2 generation is of import in inbreeding in order to maintain stable traits over generations.
Conclusion
The F1 generation is the offset filial generation of the dihybrid cross. Basically, the parents used in a dihybrid cross are identical hybrid for two traits. Also, the genotype of the F1 generation is heterozygous for both traits. However, its phenotype shows dominant phenotypes of both traits. Therefore, F1 generation shows hybridization and its method of breeding is outbreeding. In contrast, the F2 generation is the second filial generation of the dihybrid cantankerous, producing through interbreeding of individuals of the F1 generation. Normally, the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation is of ix:3:3:1 with more similar phenotypes to the P generation. Thereby, the F2 generation is important for the maintenance of parental traits over several generations. On that account, the master divergence betwixt F1 and F2 generation is the characteristics and importance of genotypes and phenotypes of each generation.
References:
1. Hyatt, Donald Due west. "WHAT'S THE DIFFERENCE Betwixt F1 AND F2?"JARS v59n4, Available Here.
Prototype Courtesy:
1. "Dihybrid Crosses" Past Sonaallii – Own work (CC By-SA iv.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. "Figure 12 03 02" By CNX OpenStax (CC Past 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia

F1 Generation And F2 Generation,
Source: https://pediaa.com/what-is-the-difference-between-f1-and-f2-generation/
Posted by: alexanderdellittef1972.blogspot.com


0 Response to "F1 Generation And F2 Generation"
Post a Comment